|
2. Type - ping 216.211.97.2 ( K-Net DNS Server ) at the prompt.
Check to see if you received four replies.
If you did not receive the replies, you can verify that TCP/IP
has initialized on your computer.
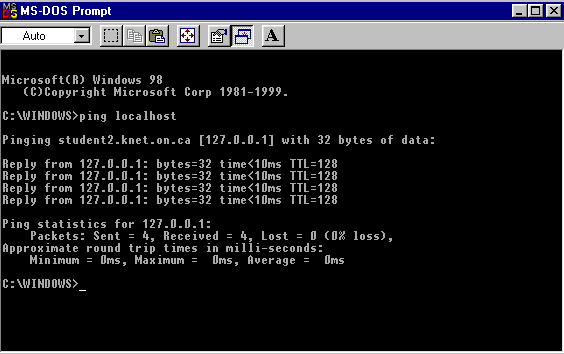
Type - ping localhost.
Localhost is a reserved host name that maps to a reserved IP address
(127.0.0.1) that represents your computer. When you type ping localhost,
the messages are local to your computer; no packets are sent to
the network. If pinging localhost is successful, you receive four
replies from IP address 127.0.0.1. If the ping command is unsuccessful
you will receive a message that says localhost is unknown. If this
happens, verify that you installed TCP/IP, and that you restarted
the computer after the installation.
|

